Oral cancer can literally wipe the smile off your face…

Smoking can even let a crow in deep relation with beautiful woman
Oral cancer can literally wipe the smile off your face…
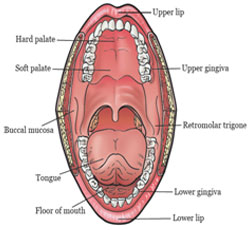
- The oral cavity includes the lips, buccal mucosa, teeth, gingiva, anterior two-third of tongue, floor of the mouth and hard palate.
- Oral cancer is defined as the cancer of lips, mouth and tongue.
What is the burden of disease in India?
- India has one third of oral cancer cases in the world.
- In India, 20 per 100000 population are affected by oral cancer which accounts for about 30% of all types of cancer.
- Over 5 people in India die every hour everyday because of oral cancer.
- Oral cancers in India estimated (Globocan, 2018)
- New cases: 1,19,992
- Deaths: 72,616
- In general, more men suffer and die from oral cancer than women.
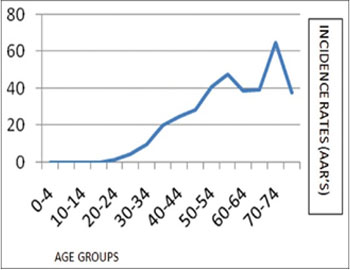
Incidence and Age
Are you at risk!
- Tobacco and beetle nut/areca nut(supari) consumption
- Alcohol consumption
- Sharp teeth or ill fitting dentures
- Diet
- Human Papillomavirus (HPV)
- Weak immune system: HIV
- Exposure to sun’s ultra violet rays
Tobacco and beetle nut/areca nut(supari) consumption
- All forms of tobacco, including cigarettes, beedi, pipes, cigars, and chewing (smokeless) tobacco.
- Keeping tobacco quid inside mouth Paan with betel nut/areca nut (supari) a


- Estimates indicate 57% of men and 11% of women between 15- 49 years of age use some form of tobacco
- More than 90% of OC cases report using tobacco products.
- Beedi>cigar
- Women chewing tobacco 10 or more times a day have risk 9.2 times that of non-tobacco chewers irrespective of age of initiation of tobacco chewing.
Alcohol consumption
- Alcohol increases the risk of oral cancer.
- The risk is about twice as high in people who have 3 to 4 alcoholic drinks per day compared to those who don’t drink alcohol.
- The risk of oral cancer is even higher in people who use both alcohol and tobacco.
- A study in India has found that alcohol consumption increases the incidence by 49% among current users and 90% in past drinkers.
- Any level of alcohol consumption, even one drink per day, increases the relative risk of developing each of these cancers.

Sharp teeth or ill fitting dentures
- Chronic irritation of gums and cheek by ill fitting dentures or sharp teeth
- Produces chronic irritation and lead to changes in overlying epithelium
- Patients wearing dentures for more than 15 years and not visiting a dentist regularly was highly associated with Oral cancer.
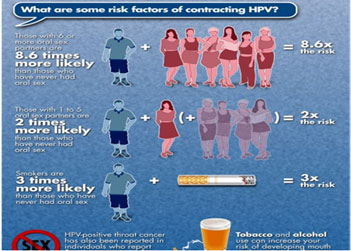
Human Papillomavirus (HPV)
- HPV infection increases the risk of certain types of oral cancer, especially in younger people.
- It is estimated that 35% of oral cancers are infected with HPV.
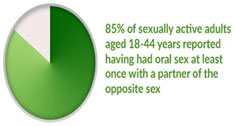
- Association between oral sex and oral cancer.


Sun exposure
- Sun exposure at early age related to men’s SCC.
- Life time sun exposure related to women’s SCC.

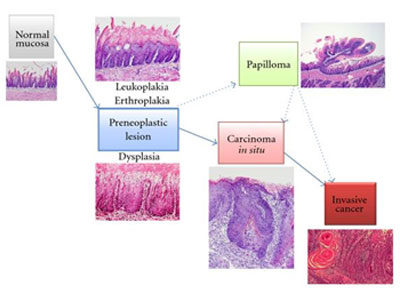
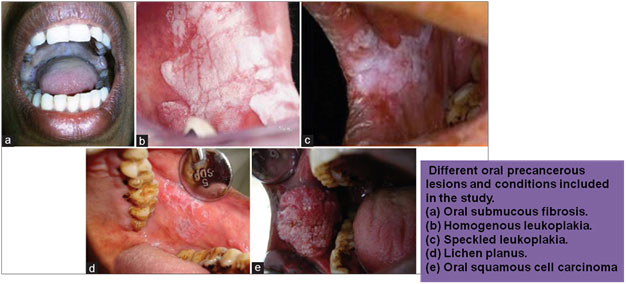
What kind of precancerous conditions?
When should you consult doctor?
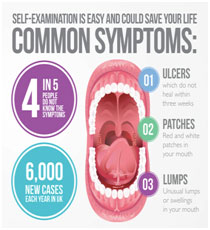
- A persistent sore in the mouth or face which does not heal.
- Difficulty or decrease in opening the mouth.
- Development of white, red or mixed patches on tongue, gums or inner linings of mouth.
- A lump or hard mass in the neck.
- Chronic pain in mouth, tongue/jaw pain.
- Difficulty in chewing or swallowing.
- Swelling, thickening, lumps or bumps on lips, gums or inner cavity of mouth.
- Unexplained bleeding in mouth.
- Hoarseness or change in voice.
- Loose teeth and ill-fitting dentures.
- Unexplained weight loss.
Are there test for early detection?
- Any cancers of the oral cavity have a long early pre-cancer period.
Oral visual Examination
You can examine your mouth yourself by looking at your mouth with the help of mirror in bright light, for early detection of oral cancers.
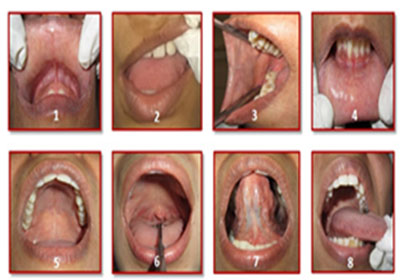
- Wash your hands thoroughly
- Explore your mouth with your finger
- Tilt your head back; examine the roof of your mouth for any abnormal thickening.
- Pull the cheeks on one side at a time, inspect the inner surface and back of the gums.
- Pull out your tongue and hold it with finger upwards, inspect and feel the floor of the mouth and look carefully at the tongue.
- Feel on both sides of the neck for any lump or enlarged lymph nodes.
If you detect any abnormality, bring it to the notice of your doctor for further evaluation
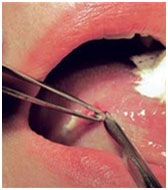
How physician diagnose
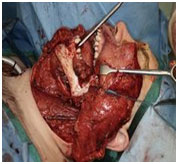
Biopsy
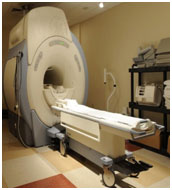
staging
Plan management
Modalities of Treatment